NPSH (Net Positive Suction Head) - Net hydraulic head (cavitation head). It is measured by the height of the liquid column at the pump suction and has the dimension "m liquid column", or for water "m water column - m water column". It is extremely important to consider this parameter when installing the pump in the centrifugal pump system.
Distinguish:
- NPSHr is the required head at the pump suction connection;
- NPSHa is the available head at the pump suction connection.
- NPSHr is the required head at the pump suction inlet to compensate for all pressure losses in the pump and to keep the liquid pressure above the saturated vapour pressure in the pump itself. The NPSHr allows for a 3% head loss due to possible cavitation (localised boiling of the liquid in the pump due to uneven flow). Typically, pump manufacturers provide information on the NPSHr value as a function of pump capacity on the pump performance chart.
- NPSHa - The available head at the pump suction connection is a characteristic of the system in which the pump is operating. NPSHa is equal to the difference between atmospheric pressure (or absolute pressure in a closed system), the suction height of the pump and the saturated vapour pressure. The figures show 4 types of systems, and for each type, the formulas for calculating the system's NPSHa are given. It is also important to take into account the density of the liquid and to convert all values to the same unit.
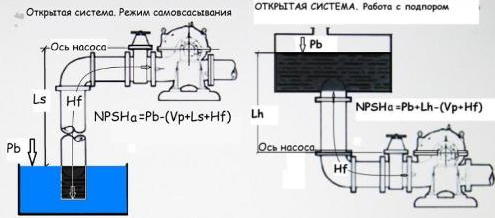
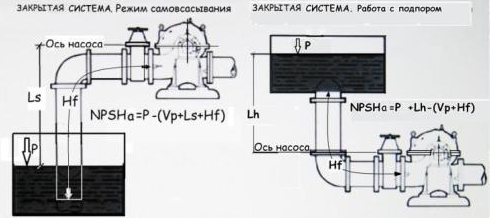

Pb = atmospheric pressure, in metres;
Vp = Saturated vapour pressure of the liquid at the maximum operating temperature of the liquid, in metres;
P = Pressure at the surface of the liquid in a closed container, in metres;
Ls = Maximum suction height, in metres;
Lh = Maximum height of the support, in metres;
Hf = Friction loss in the suction pipe at the required pump capacity, in metres. The available head NPSHa must exceed NPSHr. Preferably by 0.5 m (recommended margin). In an actual system, the NPSHa is determined by means of a pressure gauge installed on the suction side of the pump.
